SpaceX’s October Triumph: Starship Success and a Historic $733 Million Contract
In a month that will be etched in the annals of space history, SpaceX has achieved remarkable feats that have left the world in awe. October has been a banner month for the aerospace giant, marking significant milestones and securing one of the largest contracts in its history. The recent success of the Starship test flight, culminating in the unprecedented catch of the booster by the Mechazilla tower, has not only demonstrated SpaceX’s technological prowess but has also paved the way for a massive new deal with the U.S. government.
The Starship Test Flight: A Historic Achievement
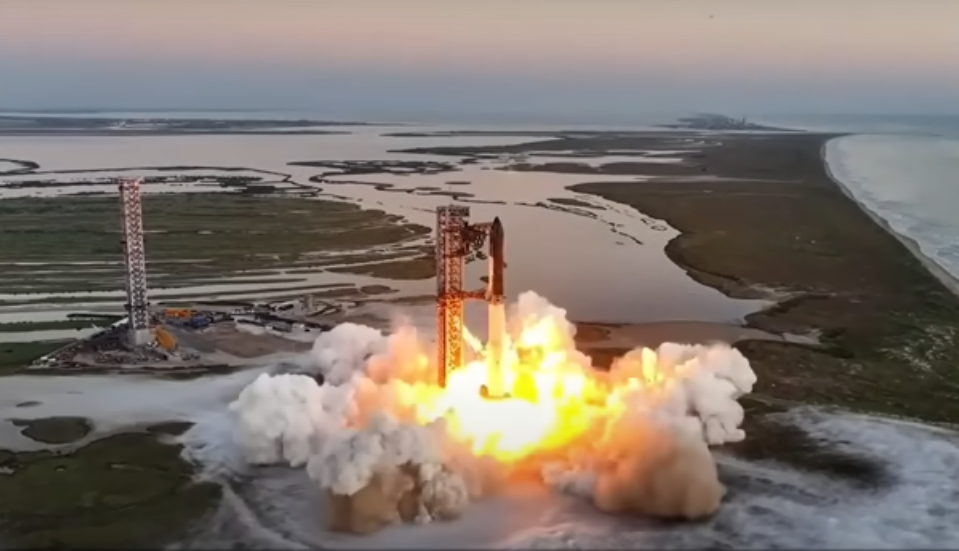
The journey to this monumental achievement began with the fifth test flight of SpaceX’s Starship. After numerous delays and regulatory hurdles, the pressure was immense. The liftoff was smooth, and as Starship ascended into the sky, it marked a significant milestone. However, the real marvel came later when the booster was successfully caught by Mechazilla, an enormous tower designed specifically for this purpose.

Catching a booster in midair is akin to threading a needle while moving at supersonic speeds. This was not just a technical achievement; it was a clear demonstration that SpaceX had mastered something no one else had even attempted on this scale. The sight of the booster being grabbed and gently lowered was nothing short of historic, and the world watched in shock and amazement.
The Ripple Effect: Social Media and Industry Reactions
The immediate aftermath of this success was a flood of reactions on social media from space enthusiasts and competitors alike. The flawless execution of the booster catch showed that SpaceX was miles ahead in the space game. This success was more than just a win for SpaceX’s technical team; it naturally drew attention and more business.
The $733 Million Contract: A Testament to Trust
Following the Starship success, SpaceX landed one of the biggest contracts in its history. The U.S. government, through the Space Force, awarded SpaceX $733 million for national security space missions. These missions are critical, involving top-secret satellites and other military assets that require absolute reliability.
These contracts, Task Order 7 and Task Order 8, will use SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rockets. Task Order 7 involves launching the USSF-124 payload from Kennedy Space Center in 2026, while Task Order 8 will see the USSF-62 mission launch from Vandenberg in 2026-2027. These missions will deploy crucial national security assets, enhancing satellite communications, surveillance, and missile warning systems for the United States.
Why Falcon Heavy?
The Falcon Heavy is currently SpaceX’s workhorse for large payloads, and its performance is unrivaled. Composed of three reusable cores, it generates over 5 million pounds of thrust at liftoff—equivalent to 18 Boeing 747s at full power. It can lift up to 63.8 metric tons to low Earth orbit and 26.7 metric tons to a geostationary transfer orbit. For missions to Mars, Falcon Heavy can send 16.8 metric tons, making it one of the most powerful rockets currently flying.
However, while Falcon Heavy is ideal for today’s missions, it is still constrained by size and capacity compared to what Starship promises. Starship, once operational, will dwarf Falcon Heavy in every category, designed to lift over 150 metric tons to low Earth orbit, potentially doubling what Falcon Heavy can do when fully reusable.
The Future: Starship’s Potential
The recent Starship test flights have shown immense potential, but they are still prototypes. The Starship Super Heavy combo completed its latest test flight on October 13, 2024. While the flight was a success, catching the booster and achieving other milestones, more work needs to be done before Starship becomes fully operational for high-stakes missions like those Falcon Heavy is currently handling.
SpaceX has been iterating rapidly on Starship prototypes, with significant improvements from the early SN series, which saw several crashes and explosions during landing tests. The current focus is on refining the booster-catching process and ensuring the spacecraft can reliably return to Earth after missions.
Looking Ahead
SpaceX plans to continue testing Starship throughout 2025, with a key milestone expected in 2025—a demonstration of orbital refueling. This is a critical step for Starship’s longer missions, such as those to Mars or the Moon. Once this process is perfected, Starship will be capable of transporting over 150 metric tons of cargo beyond Earth’s orbit, something Falcon Heavy can’t achieve without expending stages.

Competitor Struggles: Boeing’s Starliner Program
While SpaceX continues to achieve unprecedented milestones, Boeing’s Starliner program remains mired in problems and delays. The most recent embarrassment came in June 2024, when Boeing launched Starliner on a mission to the International Space Station. What was supposed to be an 8-day mission turned into a much longer stay due to significant issues with Starliner’s thruster system and helium leaks.
These technical problems became apparent after Starliner docked with the ISS, leading NASA to delay plans for the astronauts to return on Starliner. Eventually, NASA decided that Starliner was not safe enough to carry the astronauts back to Earth, forcing the agency to opt for an uncrewed return of the spacecraft. As a result, astronauts Butch Wilmore and Sunita Williams, who have now been aboard the ISS for months, will remain there until early 2025, brought back by a SpaceX Crew Dragon capsule during the Crew-9 mission.
Boeing’s Ongoing Struggles
Boeing’s corporate mismanagement has only worsened the situation. CEO David Calhoun increased his salary to $35 million despite Boeing’s ongoing troubles, including the Starliner delays and the company’s broader issues with the 737 Max crisis. Many within the aerospace community have criticized Boeing for prioritizing profits over safety, a sentiment echoed in the continued failures of the Starliner program.
The Human Element: Astronauts’ Extended Stay
Throughout the delays and technical issues with Boeing’s Starliner mission, many people wondered how astronauts Butch Wilmore and Sunita Williams felt about being stranded on the ISS. Their reactions were more understanding than expected, highlighting their commitment to the mission despite being stuck much longer than anticipated.
The Path Forward
SpaceX’s continued success and Boeing’s struggles highlight the shifting landscape of the aerospace industry. While SpaceX pushes the boundaries of space travel with groundbreaking achievements like the recent Starship test flight, Boeing must address its significant issues to remain a viable competitor.
Conclusion
As SpaceX continues to reach new heights, the future of space exploration looks promising. With the recent Starship success and the massive $733 million contract, SpaceX is poised to lead the way in advancing human spaceflight and securing national security assets. Meanwhile, the aerospace community watches closely as Boeing works to overcome its challenges and restore confidence in its capabilities.
FAQ
Q1: What was the recent significant achievement of SpaceX? A1: The recent significant achievement of SpaceX was the successful test flight of Starship and the unprecedented catch of the booster by the Mechazilla tower.
Q2: What contract did SpaceX secure following their Starship success? A2: Following the Starship success, SpaceX secured a $733 million contract from the U.S. government for national security space missions.
Q3: What rockets will SpaceX use for the new contracts? A3: SpaceX will use Falcon Heavy rockets for the new contracts, specifically for Task Order 7 and Task Order 8.
Q4: Why is Falcon Heavy significant for these missions? A4: Falcon Heavy is significant for these missions due to its unrivaled performance in lifting heavy payloads, generating over 5 million pounds of thrust, and its proven reliability.
Q5: What are the future plans for SpaceX’s Starship? A5: SpaceX plans to continue testing Starship throughout 2025, with a key milestone being the demonstration of orbital refueling, which will enable longer missions such as those to Mars or the Moon.
Q6: What issues has Boeing’s Starliner program faced recently? A6: Boeing’s Starliner program has faced significant technical issues, including thruster system failures and helium leaks, which have led to delays and the extended stay of astronauts Butch Wilmore and Sunita Williams on the ISS.
Q7: How has Boeing’s management responded to these challenges? A7: Boeing’s management, led by CEO David Calhoun, has faced criticism for prioritizing profits over safety, despite ongoing troubles with the Starliner program and other issues like the 737 Max crisis.
Q8: What is the current role of SpaceX’s Crew Dragon capsule? A8: The SpaceX Crew Dragon capsule is currently responsible for bringing astronauts back to Earth from the ISS, as seen in the planned Crew-9 mission for early 2025, which will return astronauts Wilmore and Williams.
Q9: How do these developments impact the future of space exploration? A9: These developments highlight SpaceX’s leadership in space exploration and the importance of continued innovation and reliability in advancing human spaceflight and securing national security assets.
Q10: What is the significance of orbital refueling for SpaceX’s Starship? A10: Orbital refueling is crucial for enabling longer missions beyond Earth’s orbit, such as missions to Mars or the Moon, by allowing Starship to transport over 150 metric tons of cargo, which is not possible with current rockets like Falcon Heavy.












1 comment